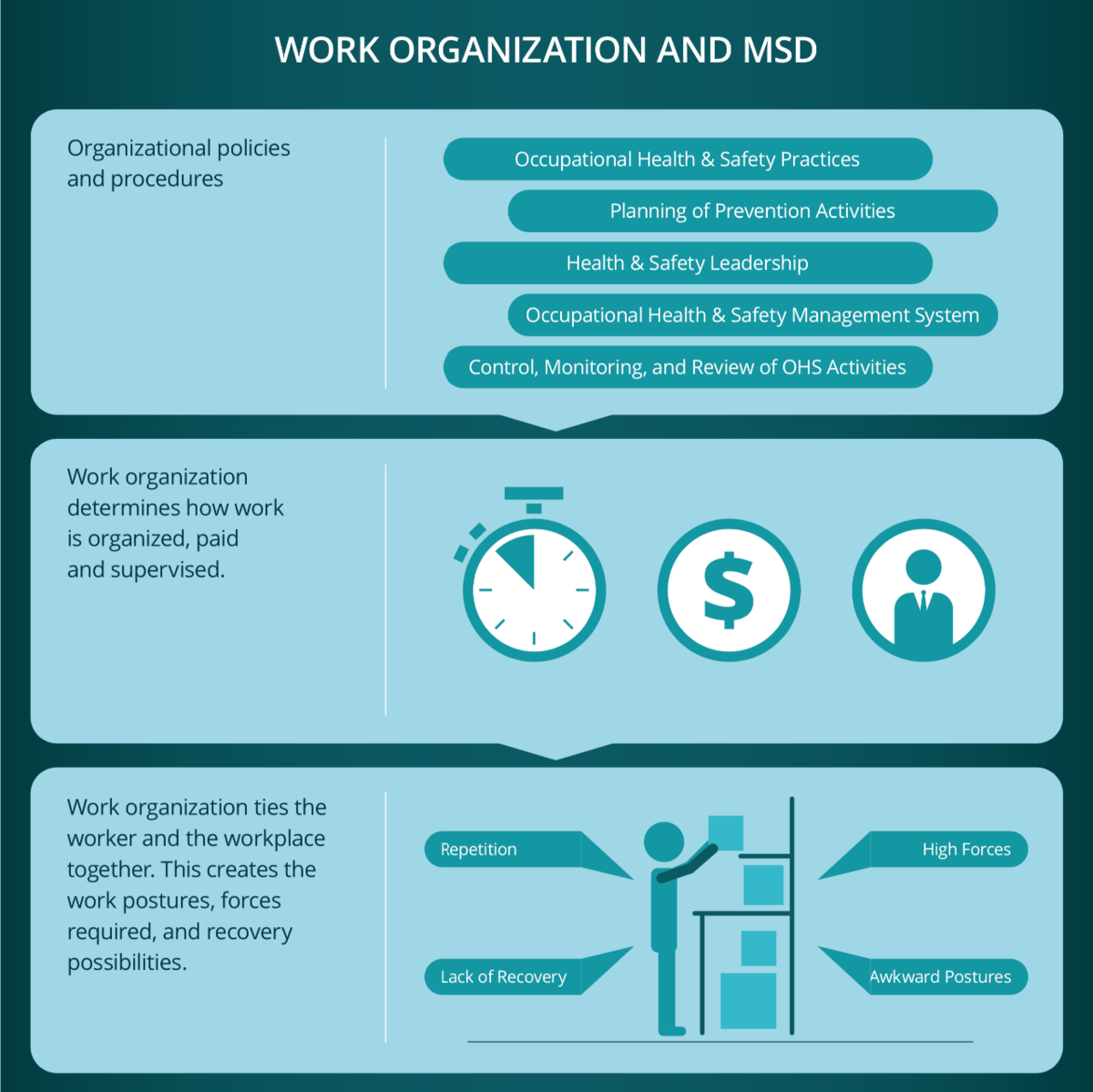
Work Organization is defined as the way work is structured, distributed, processed and supervised.
When it comes to Identifying an MSD hazard or performing a Risk Assessment, it is important to know how the job or how the work is organized. MSD hazards may be due to the design of the workspace but the work organization may minimize or magnify their effects.
A low work table may not necessarily increase the risk of developing MSD if a worker only works there briefly during the day. But if the job description (a part of work organization) dictates that the worker must work all day at that table with minimum breaks, the low table becomes a clear hazard.
Work Organization determines how the worker and workplace interact. MSD Hazards may emerge from this interaction.
During a root cause analysis or a 5Why investigation of an MSD hazard, consideration of the work organization is critical.
Details of the work organization can be found in procedures, Standard Operating Procedures (SOP), Human Resources documents, wage policies, etc.
Work organization determines to a large extent who, what, where, when and how the worker and workplace interact. MSD Hazards may emerge from this interaction.
Using an example from Health Care:
- Who does the task: Which person or team transfers the patient?
- What is the task: What transfer is needed? For toileting or repositioning?
- Where does the task take place: Is the task performed in a corridor or a toilet stall?
- When is it done: On nightshift or dayshift?
- How is the task done: Are safe work practices available? Is there a “no lift” policy?
Asking about who, what, where, when and how may also be helpful in a Root cause analysis or 5Why.

Want to search the resource library?
Find all the available resources on the MSD prevention website, including posters, videos, and links to relevant websites.

